Get the Right Care

weight loss surgery
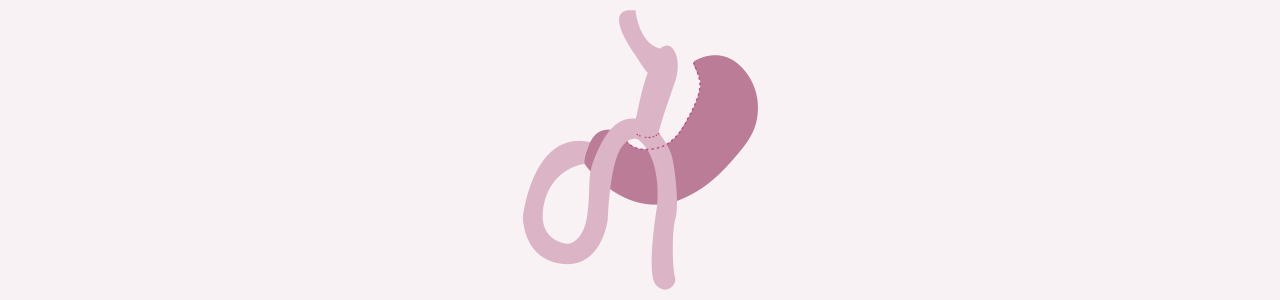
The mini gastric bypass (MGB) combines gastric reduction with a strategic intestinal bypass to promote significant and lasting weight loss. During the procedure, a small gastric pouch is created near the esophageal sphincter, and the surgeon connects it to a loop of the small intestine further downstream. This rerouting causes food to bypass a substantial portion of the small intestine, reducing the surface area available for calorie and nutrient absorption.
In addition to limiting absorption, the MGB also alters gut hormone signaling, which helps regulate appetite and improve metabolic health. The result is an earlier sense of fullness and better long-term weight management. While it shares similarities with the traditional gastric bypass (GB), the mini gastric bypass involves fewer intestinal connections, making it a simpler yet highly effective alternative.
Patients typically experience a reduction in hunger, significant weight loss, and metabolic improvements, particularly in conditions like type-2 diabetes, hypertension (high blood pressure), and sleep apnea.
The primary difference between mini gastric bypass (MGB) and traditional gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) lies in surgical complexity. The MGB requires only one connection (anastomosis) between the stomach and small intestine, whereas the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass involves two. This reduces operative time, lowers anesthesia exposure, and some studies suggest a lower risk of internal hernia, but this remains debated, though other risks like bile reflux may be more common.
Both procedures lead to sustained weight loss and improvements in obesity-related metabolic conditions. A consultation with your surgeon is necessary to find the best option for you.
A suitable candidate for mini gastric bypass weight loss surgery usually has a higher body mass index (BMI) and is struggling with chronic obesity. Generally, individuals with a BMI of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 to 39.9 along with obesity-related health issues, are prime candidates for these weight loss procedures.
Potential candidates need a mindset ready for lifestyle changes. Although the mini gastric bypass procedure aims to spark fast weight loss, it still demands commitment—especially regarding nutrition. You will be asked to follow our surgery guidelines before and after your operation. Factors like overall health, age, and willingness to make diet changes play a role in candidacy for this major step on a weight loss journey. Long-term follow-up and commitment to vitamin and mineral supplementation are also critical for success and safety.
For a detailed breakdown of costs, visit our fees page.
Advantages
Disadvantages


